Rust Converter Primer Compatibility Tests
Introduction to Rust Converter Primer Compatibility
Rust converter primers are essential tools in the fight against corrosion, especially in industries like automotive, construction, and marine engineering. These primers chemically convert rust into a stable compound, providing a protective layer that prevents further deterioration. However, not all rust converter primers are created equal, and their effectiveness can vary depending on the surface they are applied to. This article delves into the compatibility of rust converter primers with different materials, exploring their performance on metals like steel, iron, and aluminum, as well as their interaction with painted or coated surfaces.

Understanding the Chemistry of Rust Converters
Rust converters work by transforming iron oxide (rust) into a more stable compound, typically iron tannate or iron phosphate. This chemical reaction not only neutralizes the rust but also creates a protective barrier that inhibits further corrosion. The active ingredients in these primers, such as tannic acid or phosphoric acid, play a crucial role in this process. Understanding the chemistry behind rust converters is vital for assessing their compatibility with different surfaces. For instance, some acids may react adversely with certain metals or coatings, leading to unintended consequences like discoloration or reduced adhesion.
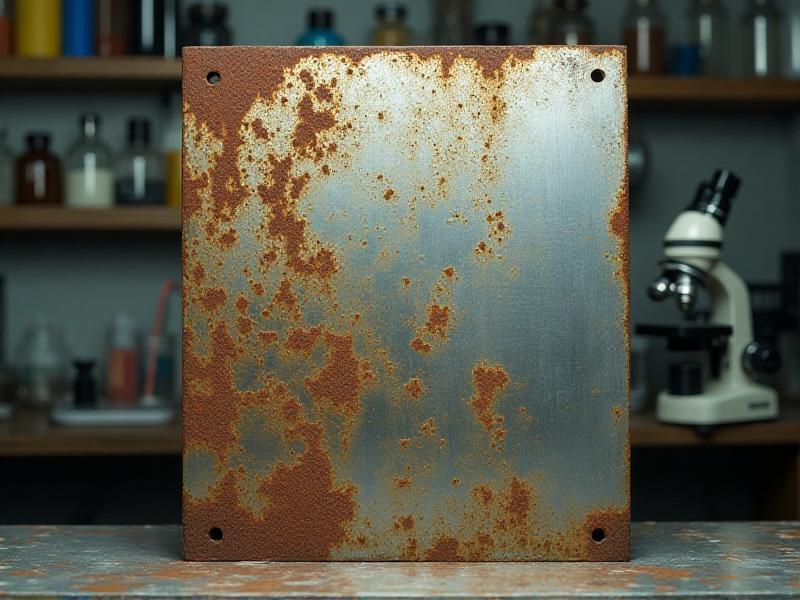
Testing Compatibility with Steel Surfaces
Steel is one of the most common materials treated with rust converter primers, given its susceptibility to corrosion. In compatibility tests, primers are applied to steel panels with varying degrees of rust, and their performance is evaluated based on factors like adhesion, coverage, and long-term protection. High-quality primers should penetrate the rust layer, convert it effectively, and form a durable, paintable surface. However, some primers may struggle with heavily corroded steel or fail to adhere properly to smooth, unrusted areas. These tests highlight the importance of choosing the right primer for specific steel applications.

Evaluating Performance on Iron and Cast Iron
Iron and cast iron surfaces present unique challenges for rust converter primers. While these materials are highly durable, they are also prone to deep, pitted rust that can be difficult to treat. Compatibility tests on iron surfaces focus on the primer's ability to penetrate and convert rust in these pits, as well as its resistance to flaking or peeling over time. Cast iron, with its porous structure, requires primers that can seal the surface effectively while maintaining its integrity. These tests reveal that not all primers are suitable for iron or cast iron, emphasizing the need for careful selection based on the material's characteristics.
Assessing Compatibility with Aluminum Surfaces
Aluminum is known for its resistance to corrosion, but it can still develop surface oxidation or rust-like deposits in certain environments. Rust converter primers designed for aluminum must be carefully formulated to avoid damaging the material's protective oxide layer. Compatibility tests on aluminum surfaces evaluate the primer's ability to neutralize oxidation without causing pitting or discoloration. These tests often reveal that specialized primers are required for aluminum, as standard rust converters may react adversely with the metal. This section underscores the importance of using the right primer for aluminum applications.
Interactions with Painted or Coated Surfaces
Rust converter primers are often used as a base coat for painted or coated surfaces, but their compatibility with existing finishes can vary. Compatibility tests focus on the primer's ability to adhere to painted surfaces without causing peeling, bubbling, or discoloration. Additionally, these tests evaluate whether the primer provides a suitable foundation for subsequent coats of paint or coating. Some primers may require sanding or surface preparation to ensure proper adhesion, while others are designed to bond directly to painted or coated surfaces. These findings highlight the need for thorough testing before applying primers to finished surfaces.
Environmental Factors Affecting Primer Performance
Environmental conditions like humidity, temperature, and exposure to chemicals can significantly impact the performance of rust converter primers. Compatibility tests often simulate these conditions to assess the primer's durability and effectiveness in real-world scenarios. For example, primers may be exposed to salt spray to evaluate their resistance to corrosion in marine environments or subjected to extreme temperatures to test their stability. These tests provide valuable insights into how environmental factors influence primer performance, helping users choose the right product for their specific conditions.
Long-Term Durability and Maintenance Considerations
While initial compatibility tests provide valuable insights, long-term durability is a critical factor in evaluating rust converter primers. Tests conducted over extended periods assess the primer's ability to maintain its protective properties and resist wear and tear. Maintenance considerations, such as the need for reapplication or additional protective coatings, are also examined. These tests reveal that some primers offer superior long-term protection, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and extending the lifespan of treated surfaces. This section emphasizes the importance of considering long-term performance when selecting a rust converter primer.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rust Converter Primer
Selecting the right rust converter primer requires careful consideration of factors like material compatibility, environmental conditions, and long-term durability. Compatibility tests provide valuable insights into how different primers perform on various surfaces and under specific conditions. By understanding these factors, users can make informed decisions that ensure effective rust prevention and long-lasting protection. Whether treating steel, iron, aluminum, or painted surfaces, choosing the right primer is essential for achieving optimal results.








