Reverse Electrolysis for Delicate Parts
Introduction to Reverse Electrolysis
Reverse electrolysis is a fascinating process that has gained traction in various industries, particularly for the treatment of delicate parts. Unlike traditional electrolysis, which involves the decomposition of substances using electric current, reverse electrolysis focuses on the removal of contaminants and the restoration of materials. This technique is especially valuable for delicate components that require precision and care, such as those found in electronics, medical devices, and historical artifacts. By understanding the principles and applications of reverse electrolysis, we can appreciate its potential to revolutionize the way we maintain and restore sensitive materials.

The Science Behind Reverse Electrolysis
At its core, reverse electrolysis involves the use of an electric current to drive ions in the opposite direction of traditional electrolysis. This process is typically used to remove unwanted substances, such as rust, corrosion, or other contaminants, from the surface of materials. The key to its effectiveness lies in the precise control of voltage, current, and electrolyte composition, which allows for targeted treatment without damaging the underlying material. By leveraging the principles of electrochemistry, reverse electrolysis can achieve remarkable results in cleaning and restoring delicate parts, making it an invaluable tool in industries where precision is paramount.
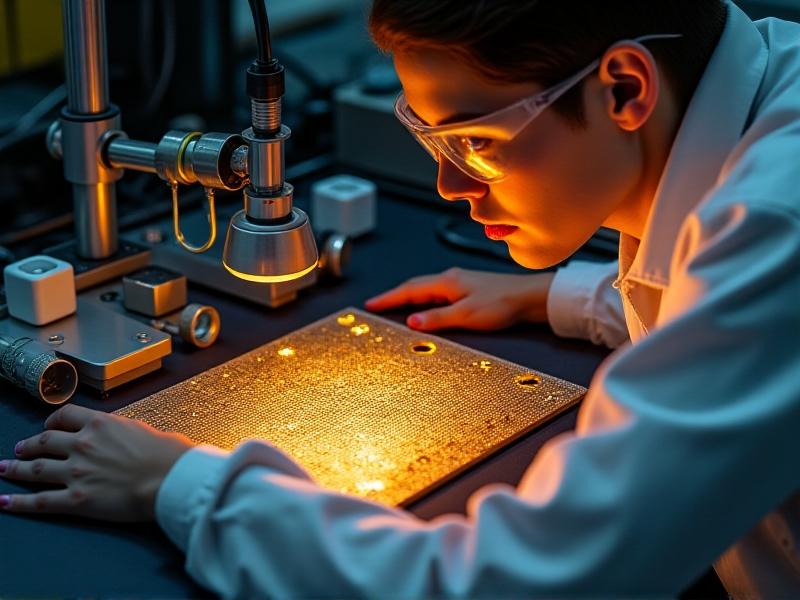
Applications in Electronics and Microfabrication
In the realm of electronics and microfabrication, reverse electrolysis plays a crucial role in the maintenance and repair of delicate components. Circuit boards, microchips, and other electronic parts are often susceptible to corrosion and contamination, which can impair their functionality. Reverse electrolysis offers a non-invasive method to remove these impurities, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic devices. Additionally, this technique is used in the production of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), where precision and cleanliness are essential. By integrating reverse electrolysis into manufacturing and maintenance processes, the electronics industry can achieve higher standards of quality and performance.

Restoration of Historical Artifacts
Reverse electrolysis has also found a niche in the conservation and restoration of historical artifacts. Many ancient objects, such as coins, tools, and jewelry, suffer from centuries of corrosion and decay. Traditional restoration methods can be harsh and risk damaging these precious items. Reverse electrolysis, however, provides a gentle yet effective solution to remove corrosion without altering the artifact's original structure. This technique has been successfully employed in museums and archaeological projects worldwide, helping to preserve our cultural heritage for future generations. The ability to restore delicate artifacts with such precision underscores the versatility and importance of reverse electrolysis in the field of conservation.
Medical Device Maintenance
In the medical field, the maintenance of delicate instruments and devices is critical to ensuring patient safety and effective treatment. Surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment are often exposed to bodily fluids and other contaminants that can compromise their functionality. Reverse electrolysis offers a reliable method to clean and sterilize these items without causing damage. This technique is particularly useful for complex devices with intricate parts that are difficult to clean using traditional methods. By incorporating reverse electrolysis into medical device maintenance protocols, healthcare providers can enhance the durability and performance of their equipment, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
While reverse electrolysis offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. The process requires precise control of parameters such as voltage, current, and electrolyte composition, which can be difficult to achieve consistently. Additionally, the cost of specialized equipment and the need for skilled operators can be barriers to widespread adoption. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements are paving the way for more efficient and accessible reverse electrolysis methods. Future developments may include automated systems, improved electrolyte formulations, and expanded applications in new industries. As we continue to explore the potential of reverse electrolysis, it is clear that this technique holds great promise for the treatment of delicate parts across various fields.








