Babbitt Metal Bearing Restoration
Introduction to Babbitt Metal Bearings
Babbitt metal bearings have been a cornerstone in machinery for over a century, offering exceptional load-bearing capabilities and durability. Named after Isaac Babbitt, who patented the alloy in 1839, these bearings are made from a soft metal matrix, typically composed of tin, antimony, and copper. Their unique composition allows them to reduce friction and wear, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Despite their longevity, Babbitt bearings can degrade over time due to factors like misalignment, contamination, or excessive load. This article delves into the restoration process, offering a comprehensive guide to reviving these essential components.
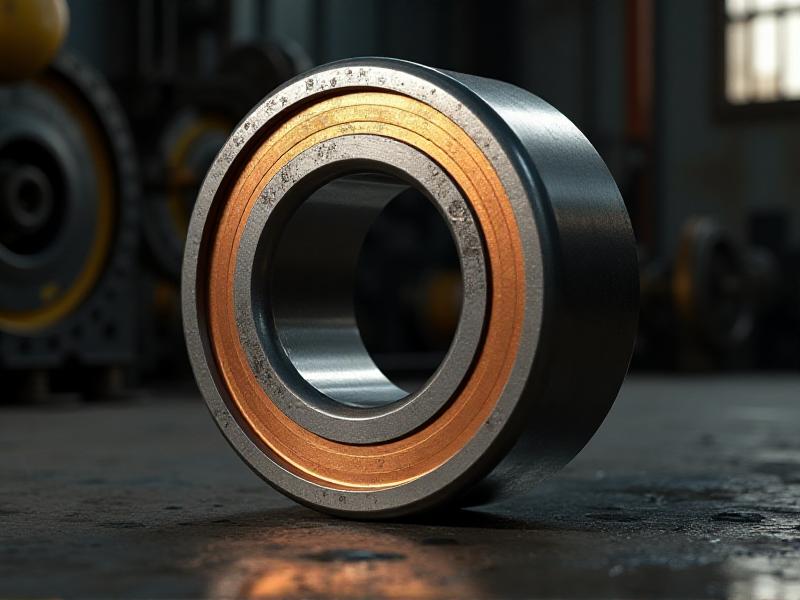

Understanding the Composition of Babbitt Metal
To effectively restore Babbitt metal bearings, it’s crucial to understand their composition. Babbitt metal is a soft alloy, primarily made of tin (90%), antimony (7%), and copper (3%). This combination provides a balance of hardness and malleability, allowing the bearing to conform to the shaft while maintaining structural integrity. The softness of the metal reduces friction, while the copper adds strength and heat resistance. Understanding this composition is vital for selecting the right restoration techniques and materials. For instance, using incompatible alloys during repairs can lead to premature failure or reduced performance.
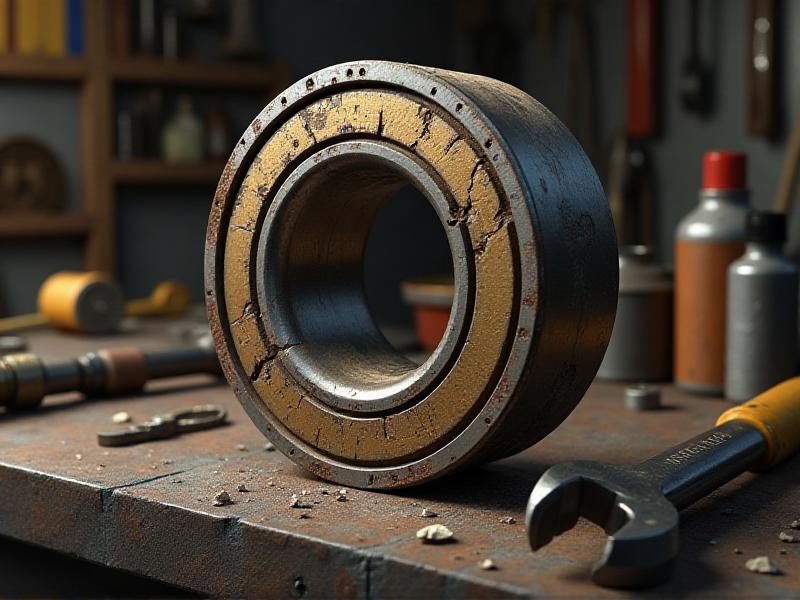
Common Causes of Babbitt Bearing Failure
Babbitt bearings can fail for various reasons, and identifying the root cause is the first step in restoration. Common issues include misalignment, which causes uneven wear; contamination from dirt or debris, leading to scratches and pitting; and overheating, which can soften the metal and reduce its load-bearing capacity. Additionally, improper lubrication or excessive load can accelerate wear and tear. By diagnosing the specific cause of failure, you can tailor the restoration process to address the underlying problem, ensuring the bearing’s longevity and performance.

Tools and Materials Needed for Restoration
Restoring Babbitt bearings requires specialized tools and materials. Essential items include a bearing scraper for removing damaged material, a torch for heating the bearing during the pouring process, and a mold to shape the new Babbitt metal. You’ll also need cleaning supplies like solvents and brushes to remove contaminants. For the Babbitt metal itself, ensure you have the correct alloy composition to match the original bearing. Additionally, safety equipment such as gloves, goggles, and heat-resistant clothing is crucial to protect against burns and fumes during the restoration process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Babbitt Bearing Restoration
Restoring a Babbitt bearing involves several steps. First, remove the bearing from the machinery and clean it thoroughly to eliminate dirt and debris. Next, inspect the bearing for damage and determine the extent of restoration needed. If the damage is severe, you may need to remove the old Babbitt metal using a scraper or torch. Once the bearing is prepared, heat it to the appropriate temperature and pour the new Babbitt metal into the mold. Allow the metal to cool and solidify before machining the bearing to its final dimensions. Finally, reinstall the bearing and test it to ensure proper alignment and performance.
Tips for Maintaining Restored Babbitt Bearings
Proper maintenance is key to extending the life of restored Babbitt bearings. Regularly inspect the bearings for signs of wear or misalignment, and ensure they are adequately lubricated to reduce friction. Avoid overloading the machinery, as this can cause premature failure. Additionally, keep the surrounding environment clean to prevent contamination from dirt or debris. By following these maintenance tips, you can maximize the performance and longevity of your restored Babbitt bearings, saving time and money in the long run.
The Environmental and Economic Benefits of Restoration
Restoring Babbitt bearings offers significant environmental and economic benefits. By repairing rather than replacing bearings, you reduce waste and conserve resources. Additionally, restoration is often more cost-effective than purchasing new bearings, especially for specialized or custom-made components. This approach also minimizes downtime, as repairs can often be completed more quickly than sourcing and installing new parts. By embracing restoration, industries can achieve sustainability goals while maintaining operational efficiency.
Case Studies: Successful Babbitt Bearing Restorations
Real-world examples highlight the effectiveness of Babbitt bearing restoration. In one case, a manufacturing plant restored a set of bearings in a critical piece of machinery, avoiding costly downtime and extending the equipment’s lifespan by several years. Another example involves a power generation facility that restored bearings in a turbine, improving efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. These case studies demonstrate the practical benefits of restoration, showcasing how industries can save money and resources while maintaining operational reliability.
Future Trends in Babbitt Bearing Technology
As technology advances, so do the materials and methods used in Babbitt bearing restoration. Innovations in alloy composition, such as the addition of nanoparticles, are enhancing the strength and durability of Babbitt metal. Additionally, advancements in 3D printing are enabling the creation of custom molds and components, streamlining the restoration process. Looking ahead, these trends promise to make Babbitt bearing restoration even more efficient and effective, ensuring their continued relevance in modern machinery.






